Managing Workplace Injuries: A Guide to Handling?
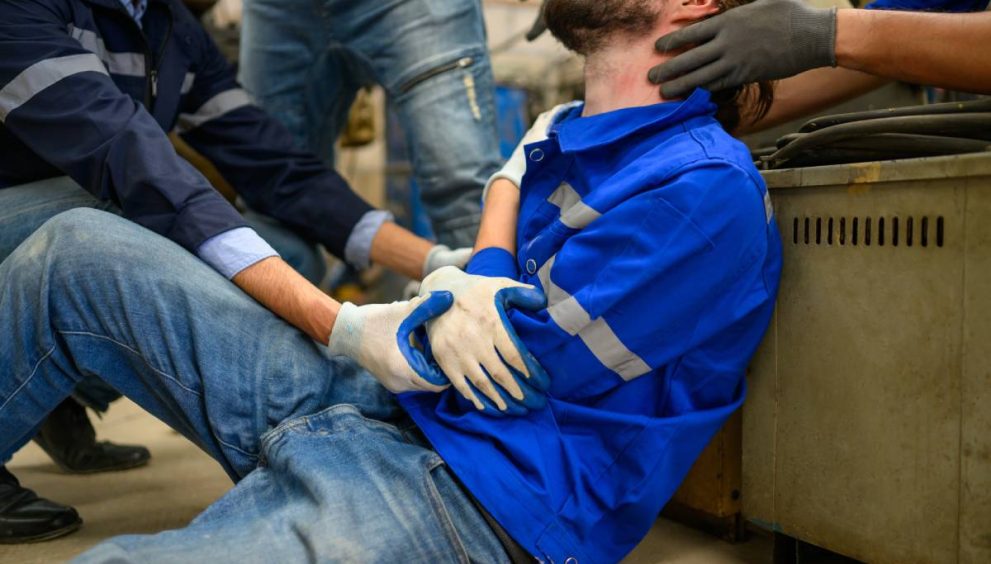

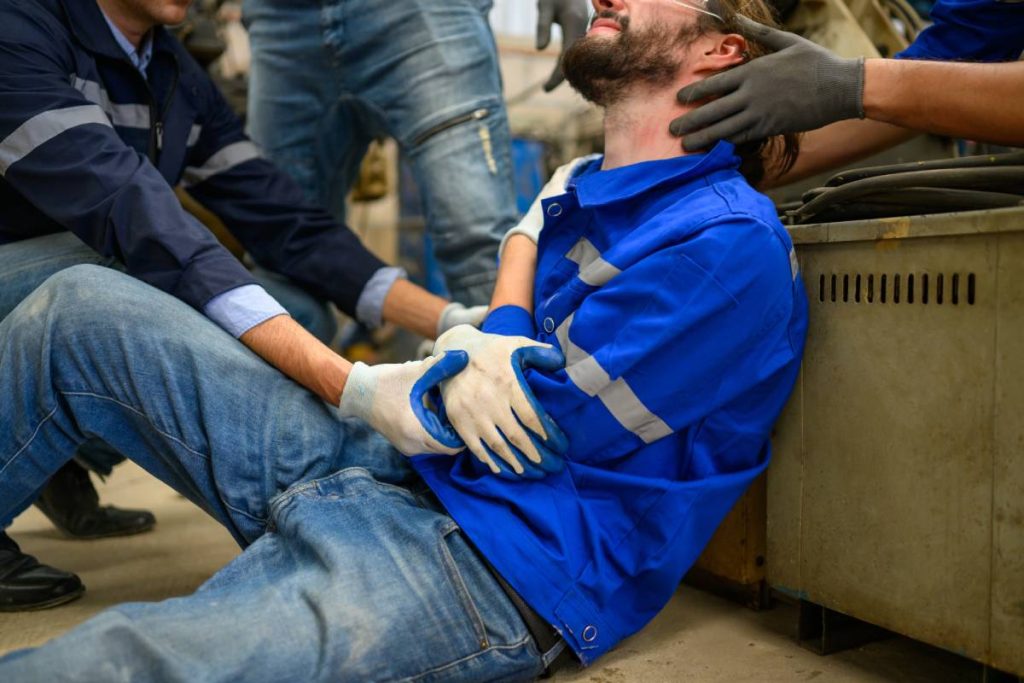
Workplace injuries can happen in any job, whether you’re lifting heavy materials on a construction site or spending long hours at a desk.
From sudden accidents to injuries that develop over time, these incidents not only affect an employee’s health but can also disrupt productivity, income, and morale.
Understanding what qualifies as a workplace injury, how to respond effectively, and how to continue working safely during recovery is essential for both employees and employers.
This article explores the definition of workplace injuries, how to handle them properly, and practical strategies for working around an injury while staying on the path to recovery.
What Is an Injury in the Workplace?
A workplace injury refers to any harm or illness that occurs as a direct result of an employee performing their job duties or being present in the work environment. These injuries can range from minor cuts and bruises to serious trauma or long-term health conditions. Common examples include:
- Physical injuries like sprains, fractures, burns, or lacerations
- Repetitive strain injuries such as carpal tunnel syndrome or tendonitis
- Occupational illnesses like respiratory conditions from exposure to hazardous substances
- Mental health injuries such as stress, anxiety, or PTSD due to workplace trauma or harassment
In many countries, workplace injuries are covered under workers’ compensation laws, which provide medical care, wage replacement, and support during recovery. It is crucial that both employees and employers understand their rights and responsibilities in these situations.
How to Handle a Work-Related Injury
Handling a work-related injury properly is vital to ensure a smooth recovery, protect legal rights, and prevent future incidents. Here is a step-by-step guide for what to do when an injury occurs:
Seek Immediate Medical Attention
Your health comes first. If the injury is serious, call emergency services right away or get to the nearest hospital.
Even if the injury seems minor, it is still important to get it evaluated by a medical professional to avoid complications later. Early treatment can prevent further damage and ensure that you recover as quickly as possible, reducing the risk of long-term issues.
Report the Injury to a Supervisor
As soon as you are safe, notify your manager or supervisor. Most companies have formal reporting procedures for workplace injuries, and some jurisdictions require you to report the injury within a specific time frame to qualify for workers’ compensation. Reporting promptly helps ensure that your employer is aware of the incident and can initiate the proper steps for investigation and documentation.
Document the Incident
Write down the details of how and when the injury happened. Include names of witnesses, photos of the scene (if possible), and any contributing factors.
This documentation will be crucial when filing a claim or if a dispute arises. Accurate records are important to establish the facts and can protect your legal rights should any questions or challenges about the injury arise later.
File a Workers’ Compensation Claim
In many countries, employees are entitled to workers’ compensation, which can cover medical bills, rehabilitation costs, and a portion of lost wages.
This process typically involves submitting a claim form and medical records to your employer’s insurance carrier. It’s important to follow up regularly to ensure your claim is being processed, as delays can impact your access to benefits and timely treatment.
Follow Medical Advice
Stick to the treatment plan given by your doctor. Failing to follow medical advice can slow your recovery and may affect your eligibility for continued compensation. Attend all follow-up appointments, therapy sessions, and prescribed treatments. Adhering to the doctor’s guidance ensures you are on track for full recovery and can prevent any setbacks in your rehabilitation process.
Communicate with Your Employer
Stay in contact with your employer throughout the recovery period. This includes providing updates on your condition and discussing potential accommodations or modified duties that may help you return to work safely.
Open communication helps maintain a positive relationship with your employer and ensures that any necessary adjustments to your workload or schedule are made to accommodate your recovery.
How Do You Work Around an Injury?
Returning to work after an injury can be both physically and emotionally challenging. In many cases, it’s possible to resume some duties while still recovering, especially if adjustments are made to the work environment or schedule. This is known as a modified or light-duty return to work.
Here are strategies for successfully working around an injury:
1. Understand Your Limitations
Before returning to work, talk to your healthcare provider about what activities are safe. Get a clear list of physical restrictions (e.g., no lifting over 10 lbs., no standing for long periods) and share these with your employer.
2. Request Reasonable Accommodations
Under laws like the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) in the U.S., employers are required to provide reasonable accommodations for injured employees. These can include:
- Adjusted workstations (e.g., ergonomic chairs, standing desks)
- Modified duties (e.g., administrative tasks instead of physical labor)
- Flexible schedules (e.g., shorter shifts or more breaks)
3. Gradual Return to Work
Sometimes a phased return is the best approach. This allows you to slowly build back your endurance and confidence. For example, you might start with part-time hours and gradually increase your workload over several weeks.
4. Use Assistive Tools or Devices
Depending on the nature of the injury, tools such as wrist braces, back supports, or voice-to-text software can help minimize strain and make working more comfortable.
5. Maintain Open Communication
Keep an ongoing dialogue with your supervisor and HR department. If your condition changes or the current work setup causes pain or stress, let them know immediately so that further adjustments can be made.
6. Focus on Mental Recovery Too
Injuries don’t just affect the body they can impact self-esteem, confidence, and mental health. If you’re feeling anxious or depressed about returning to work, don’t hesitate to seek counseling or support from employee assistance programs (EAPs). It’s essential to maintain a balanced life, managing both physical and mental health during recovery.
Preventing Future Injuries
One of the most important aspects of handling a workplace injury is learning from it. Employers and employees should collaborate to:
- Investigate the cause of the injury
- Improve safety protocols and training
- Implement ergonomic assessments or hazard reduction strategies
- Encourage a culture of safety, where workers feel empowered to report risks without fear of retaliation
Preventing future injuries not only protects workers but also enhances morale and productivity across the organization.
Conclusion
Workplace injuries can be disruptive, but with proper handling, supportive policies, and proactive adjustments, employees can recover and often return to work stronger than before.
Whether you’re an employee who’s been injured or an employer navigating a staff injury, it’s essential to prioritize safety, maintain clear communication, and follow the legal and medical processes involved.
Understanding what a workplace injury is, knowing the right steps to take when one occurs, and making adjustments to work safely during recovery are key to a healthy and resilient workforce.

 English
English